When you open a website or an application, you will see a page with different text, images, buttons, and every click will make some changes. Ever thought of how websites and applications work smoothly? From the moment you click, scroll or tap, a lot is instantly happening on your screen. Buttons respond, layouts adjust, animations play and content updates without refreshing. All these are done by front-end development, the technology behind the visual and interactive experiences we enjoy. This article serves as a complete beginner’s guide for aspiring front-end developers. Here, you will gain insights into front-end programming languages and frameworks, along with why and how you should learn front-end programming.
What is Front-end development?
Front-end development is the process of creating the visible and interactive parts of a website or application. The structure of a website, its layouts, colours, buttons, links, text, images, and how elements respond to user actions, all of this is shaped by front-end development. It also determines how smoothly users can interact with a digital product.
The goal of front-end development is to turn design ideas into meaningful digital experiences. Beyond visual appeal, it places a strong emphasis on usability and performance. In simple terms, front-end development shapes how a website looks, feels, and behaves. This is especially important today, as JavaScript powers 98.9% of all websites globally, with more than 51 million active websites relying on it as their primary client-side programming language, making it the backbone of modern front-end development.
Front-end development vs Back-end development
Front-end development makes a website usable and enjoyable to users. It focuses on the user side. Back-end development works on the server side, which the users cannot directly see or access. It manages data, logic, security, and communication between the front-end and databases. Imagine the website being a restaurant. The front-end is the waiter who shows you the menu and takes your orders, and the back-end is the kitchen where the food is prepared, but users do not have direct access.
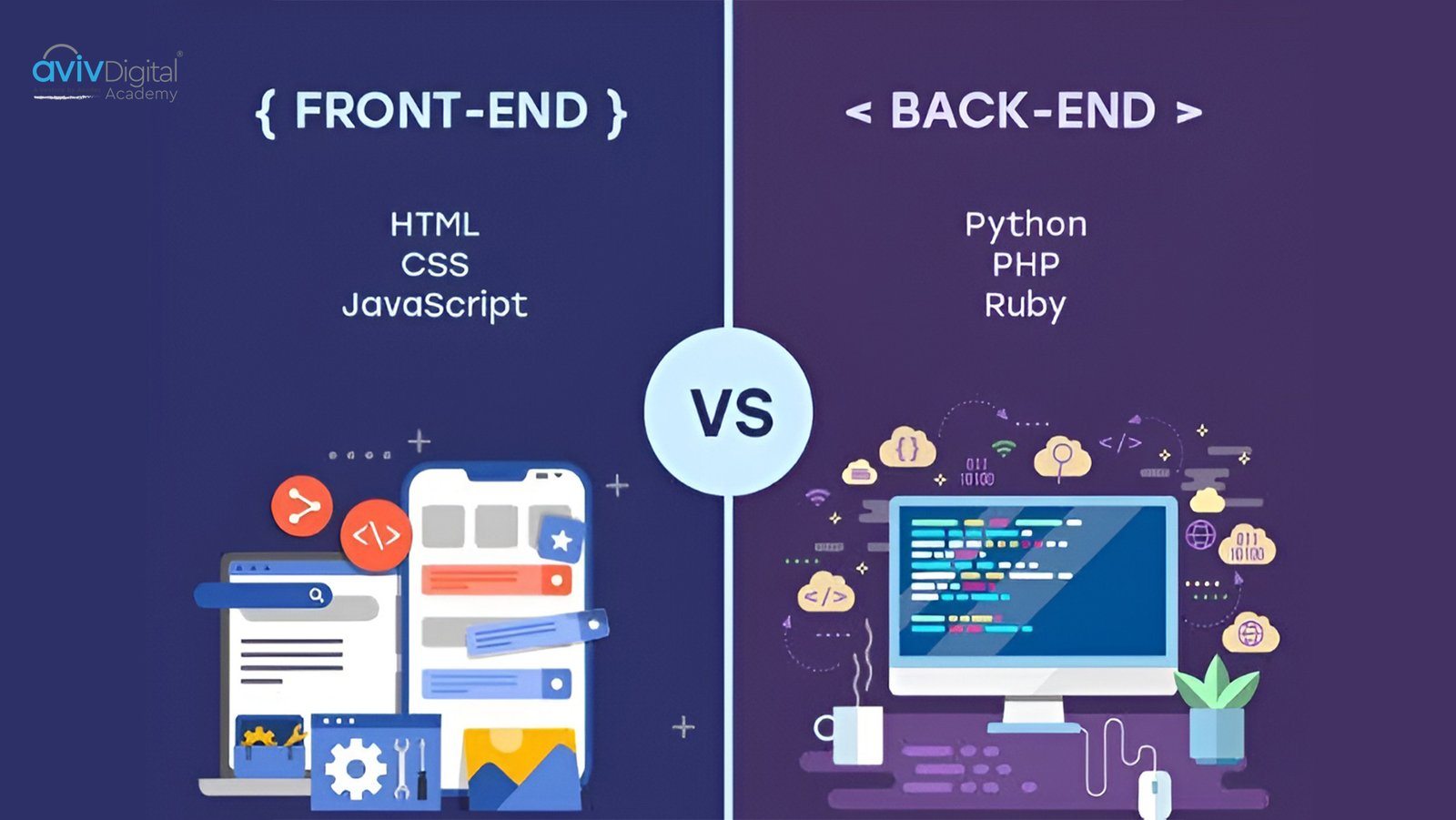
In simple words, while front-end development is the face of a website, back-end development is the brain. For a website or application to work properly, both of these are required.
Key differences between front-end and back-end :
| Front-end | Back-end |
| Builds the user-facing part | Handles clicks, scrolls, form inputs and UI behaviour |
| Focus on layouts, themes and user experience | Focus on data processing, logic and security |
| Handles clicks, scrolls, form inputs and UI behavior | Processes requests triggered by user actions |
| Core technologies are HTML, CSS, JavaScript and TypeScript | Core technologies are Python, Java, PHP and databases |
Front-end Programming Languages

Front-end programming languages are the core tools used in front-end development. These languages are used to create the basic structure, visual design and interactivity. HTML, CSS and JavaScript are the “golden trio” of front-end development. These are the core front-end languages, while a fourth emerging language, TypeScript, is also used now.
If the website is the body, then HTML is the skeleton that provides a structure, CSS is the skin that makes it look presentable, and JavaScript is the brain that is responsible for behaviour and interaction.
1. HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language)
HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language) is the most basic and essential language used to build websites. When you open a website, the texts you read, the images you see, and the links you click are all structured using HTML.
In simple words, HTML is the “backbone” of web development. Without HTML, a webpage would not have a proper layout.
When learning front-end programming, HTML is usually the first language people learn because it’s the easiest to understand and is required for every type of web design. No matter what kind of website it is, whether an e-commerce store, a blog, or a social media platform, it uses HTML in some form. In fact, using semantic HTML elements can improve SEO performance by up to 32% and increase accessibility compliance by 45%, according to recent web accessibility studies, showing why writing proper HTML matters beyond just layout.
HTML uses different elements for different content, with each element serving a specific purpose. Common elements in HTML are :
- Headings – For titles
- Paragraph – For content
- Forms – For collecting user inputs such as login or contact information
- Links – For connecting one page to another
- Images – For displaying images
- Lists – For numbered or bullet point items
Modern HTML uses semantic elements like header, footer, section and article for improving accessibility and SEO. HTML is not a programming language, but a markup language that labels content, and it cannot handle logic, perform calculations or make decisions.
Advantages and limitations of HTML
Advantages :
- Beginner-friendly
- Works on all browsers and devices
- Forms the base of all front-end frameworks
Limitations :
- Cannot create fully functional webpages on its own
- Cannot create interactive features
- Relies on CSS and JavaScript for full functionality
2. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a styling language used to design the appearance of a website. Without CSS, a webpage would look unstyled and bland. CSS turns a basic HTML page into a visually attractive one using elements such as colours, fonts, spacing and layout.
In front-end development, CSS is responsible for :
- Aligning content on the page
- Creating responsive designs for mobile, laptop and tablets
- Setting fonts and text sizes
- Choosing colours and backgrounds
There are 3 types of CSS depending on the ways they are applied :
- Inline CSS – Applied directly to an element
- Internal CSS – Written inside the webpage
- External CSS – Written separately into another file and then linked to the webpage
CSS is not a programming language but a styling language used to control the visual presentation of a webpage and does not handle logic or functionality. Today, CSS has become incredibly powerful. CSS3 features are supported by 97.4% of modern browsers, allowing developers to create advanced layouts, transitions, and animations without relying heavily on JavaScript.
Advantages and limitations of CSS
Advantages :
- Creates responsive designs
- Saves development time
- Easy to update and maintain
Limitations :
- Challenges with complex layouts
- Inconsistency across different browsers
- Cannot add interactivity on its own
3. JavaScript

JavaScript is a front-end programming language that is used to make websites interactive and dynamic. JavaScript works closely with HTML and CSS in front-end development, where HTML defines the content, CSS styles the content, and JavaScript adds behaviour & interactivity.
JavaScript is a core front-end language and is essential for building modern websites. It brings pages to life by enabling real-time interactions, dynamic content updates, and responsive user experiences. Simply put, JavaScript turns static pages into fully functional web applications. This importance is reflected in its ecosystem as well. React currently leads framework usage, with 57% of professional JavaScript developers choosing it to build interactive web applications, highlighting how central JavaScript is to modern front-end development.
Common JavaScript concepts beginners should learn include:
- Variables
- Conditions
- Loops
- Events
- Functions
Unlike HTML and CSS, which are markup language and styling language, respectively, JavaScript is a programming language as it can handle logic, perform calculations, make decisions and interact with servers.
Advantages and limitations of JavaScript :
Advantages :
- Makes websites interactive
- Supports many frameworks and libraries
- Has a large developer community
Limitations :
- Can be a bit challenging for beginners to learn at first
- Debugging can be time-consuming
- Browser differences may affect behaviour
4. TypeScript
TypeScript is a front-end programming language that runs on top of JavaScript. It helps developers create cleaner, more structured code that is less prone to errors when building next-gen web apps. TypeScript is compatible with the other essential front-end technologies, i.e., HTML, JavaScript, and CSS. Therefore, TypeScript is used to create a front-end application that is properly structured and dependable through the combination of HTML for content definition, CSS for styling, JavaScript for behaviour, and a well-structured TypeScript codebase.
TypeScript has become a preferred choice for enterprises when building scalable applications because it helps developers catch mistakes early and manage complex codebases more efficiently. In fact, TypeScript detects approximately 15% more bugs during development compared to vanilla JavaScript, which significantly reduces production-level errors. In short, TypeScript adds structure, safety, and scalability to JavaScript, making it easier to maintain and grow applications as development progresses.
The basic concepts about TypeScript that beginners should learn are:
- Types
- Interfaces
- Functions
- Classes
- Modules
One important distinction between JavaScript and TypeScript is that JavaScript determines your data types on the fly, but TypeScript requires you to define them in advance. Therefore, before you begin coding using TypeScript, you must be aware of the type of data you are working with. This facilitates early error detection and overall improves coding efficiency. To run in a browser, TypeScript code ultimately transforms into JavaScript code.
Advantages and limitations of TypeScript :
Advantages :
- Ideal for large and complex projects
- Can detect errors beforethe code runs
- Works well with JavaScript frameworks such as Angular and React
Limitations :
- A bit challenging for beginners
- Not directly supported by browsers
- Requires an additional compilation step
| Feature | HTML | CSS | JavaScript | TypeScript |
| Purpose | Structuring the content of a webpage | Designs and styles the appearance of a webpage | Adds logic and interactivity to webpages | Adds structure and safety to JavaScript |
| Role in front-end | Creates the foundation | Improves visual appearance | Controls behaviour | Improves code readability |
| Used for | Text, images, links, forms | Colours, fonts, layouts, responsiveness | Events, animations and dynamic content | Large-scale and maintainable applications |
| Browser Support | Supported by all browsers | Supported by all browsers | Supported by all browsers | Converted to JavaScript for browsers |
| Error handling | None | Limited | At runtime | Before code runs |
| Learning Difficulty | Very easy | Easy | Moderate | Slightly difficult |
Front-end Frameworks and Libraries
Front-end frameworks and libraries are tools that help developers build websites and applications faster and more efficiently. These frameworks and libraries are built upon core front-end programming languages such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and TypeScript.
A framework is a set of pre-written code that provides a structure for your application. It tells you where to put your code and how it should run. Popular front-end frameworks include Angular and Vue. Angular continues to play a strong role in enterprise development, maintaining around 25% market share in enterprise applications and recording approximately 2.5 million weekly downloads, which shows its reliability for large-scale, structured projects.
A library, on the other hand, is a collection of reusable code that developers can call when needed to perform specific tasks like handling animations, making data requests, or building individual UI components. React is one of the most popular JavaScript libraries in front-end development, with over 15 million weekly npm downloads and more than 210,000 GitHub stars. It is widely trusted, with 70.2% of developers choosing React for new projects, thanks to its flexibility and component-based approach.
The main distinction between a framework and a library is that, while a framework controls the flow of the application, a library is called by the developer, and the flow of applications is under the control of the developer.
Both frameworks and libraries are tools that are used to simplify and speed up development. They provide reusable code, ready-made structures and built-in solutions for common tasks such as handling user interactions, managing data and updating the interface.
Frameworks and libraries are used in large and complex projects, but beginners can learn them. It is better to learn front-end frameworks and libraries only after gaining a strong understanding of core front-end languages such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript and TypeScript.
Conclusion
Front-end development has a lot of influence on how your website or app will look and work. Everything users interact with, from the layout and look of the Web page to interactivity and visuals, is produced by front-end coding. How these things work together is the first step in becoming a successful front-end developer.
Simplified the front-end programming languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript and TypeScript) in this guide and learned to use them together in developing modern web UIs. HTML for the structure, CSS for visual styling, JavaScript for logic and a bit of interactivity and TypeScript when you need to handle something more complicated. These are the two that underpin everything we do as front-end developers.That being said, we have also taken a glance at front-end frameworks and libraries such as Angular, Vue or React, that have made developers’ lives easy in creating powerful web applications. Though these tools are potent, it is always better to learn the core languages first, Learning Before Frameworks and gaining mastery over them, so that when you learn about their frameworks.
There are many possibilities towards learning to become a front-end developer, especially for beginners and future developer enthusiasts. By doing things step by step, starting from solid foundations, and reaching for more advanced tools one after the other, you can create powerful, user-friendly modern web applications.
Aviv Digital Academy is one of the leading institutes that provides a full-stack development Course in Calicut. We offer a comprehensive curriculum designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge necessary to thrive in the industry. For more details, contact us at: +91 8156998844
Frequently Asked Questions
Which front-end language should I learn first?
HTML is the best language to start with, as it is the easiest and most beginner-friendly language. Its syntax is simple, with readable tags. After HTML, move on to CSS and then JavaScript.
Is TypeScript required for beginners?
TypeScript is not required at the beginner level. Learning it later can help to manage large and complex projects.
Is front-end development a good career choice?
Yes. Front-end development is one of the best career options in software development as it offers strong career opportunities due to the increasing demand for web applications across industries.






