Google Tag Manager – an amazing tool, which is a free tool making it easier to manage and deploy tags, meant for marketing. These tags comprise of either snippet of code or tracking pixels employed within your website or apps, without the need to modify the code. In the year 2020, this should be a must-have tool in every marketer’s toolkit. Actually, you can use it without hassles or without help from any web developer.
But, if you want to use it, you should have a little bit of technical knowledge or get yourself trained in the same. You can, of course, find some help online – take courses or engage in self-study Or Join an Institute which offers you best training in this filed like AvivDigital 🙂 (Self Marketing)
For instance, if you are planning to put Facebook pixels, then, you probably need to be familiar with how Facebook tracking pixels will need to fire through GTM with different events. You can easily set up event tracking in Google Tag Manager if you are proficient in how or what ‘events’ you want to track. Same way if you want to track Google Analytics Events through GTM, You should have a deep understanding of Google Analytics events; what kind of data can be used to track events; how your reports will appear in Google Analytics; and what kind of names you would use for your labels, categories, and actions.
It is imperative that you provide yourself with an in-depth understanding of all the aspects of Google Tag Manager before you start using it. Once you grab a better understanding of this, you can track an umpteen number of facts without any hassle.
Here, we will take you through the three major aspects of the Google Tag Manager: tags (JavaScript snippets or the tracking pixels), triggers (instructs the Google Tag Manager when or how it should trigger a tag to action and variables (contains any additional information needed for the tag or trigger).
Let us examine these aspects in-depth:
Tags
Tags, also known as snippets of code or tracking pixels, are acquired through third-party tools. With, the help of these tools, the Google Tag Manager is supplied with the information on what has to be done next.
Here are a few examples of these tags that Google Tag Manager employs:
- Adwords Remarketing Code
- Heat map Tracking Code
- Google Analytics Universal Tracking Code
- Facebook Pixels
- Adwords Conversion Tracking Code
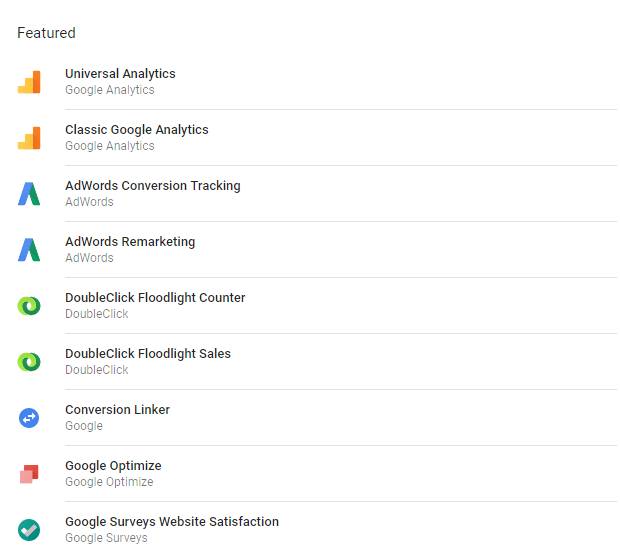
Triggers
Triggers help in triggering the action that the tags are supposed to perform. With this, the Google Tag Manager would go about the next step, including when and what the Google Tag Manager has to do. It helps you to action trigger the tags across the page view, or customize.
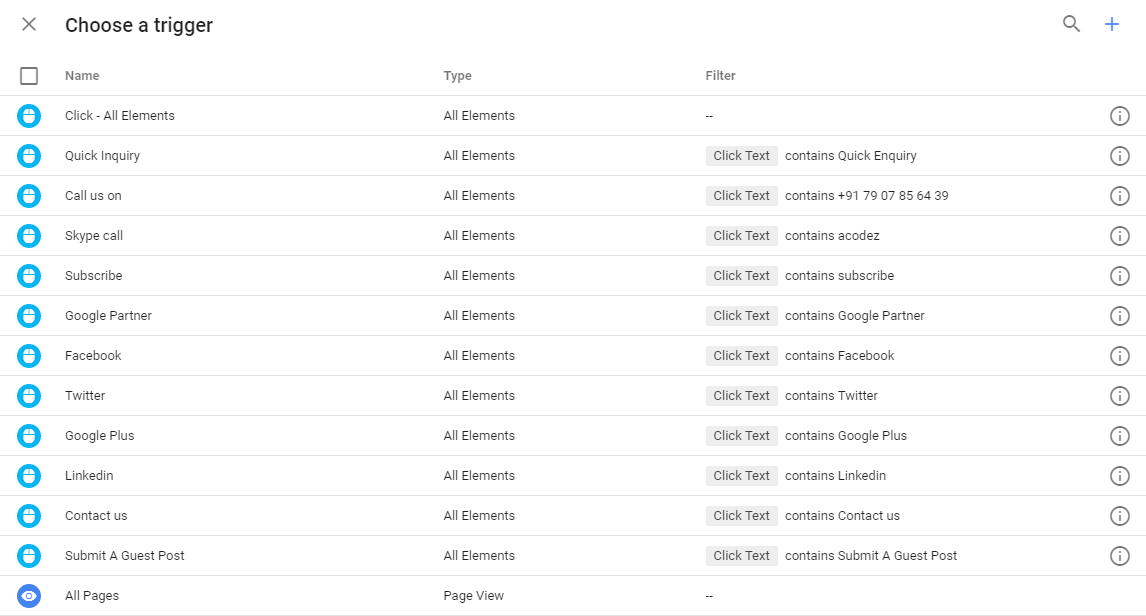
Variables
As we discussed, variables are the additional or further details that would help Google Tag Manager to tag and trigger the action. For instance, you can create Google Analytics UA number, one of the most common constant variables that are generated using Google Tag Manager.
Let us find out how Google Tag Manager differs from Google Analytics:
Google Tag Manager, as you know, is a tool that helps to manage and store third-party code. There are actually no possible documentation on how to perform analysis on Google Tag Manager.
But, you can always employ Google Analytics for reporting and analysis. The conversion filters or tracking goals are dealt using Analytics. With Google Analytics, you can manage all forms of reporting, including custom segments, e-commerce sales, time on page, engagement reports, bounce rate and more.
Precisely, we can define Google Tag Manager as the tag management system that helps in creating tags, for sending user interaction data to Google Analytics. If we call GTM as your developer person that will be wrong anyway 🙂
Google Tag Manager will help:
- Save time
- Add scalability to site implementation
- Provide ease of use
- Provide creative space for designing complex and customized tags
- A/B Testing
Here are some reasons on why you should be implementing Google Tag Manager today:
Future-proofing your website
You must be quite familiar with the Google Tag Manager that you have been using to add analytics, Adwords remarketing, conversion tracking code, Facebook pixel for your sites. And, alongside, you are also implementing the other 3rd party tracking pixel to your website. If you still do not use these or are unfamiliar with these names, then, it is still not too late before you start utilizing their benefits.
If there are a number of pages to be modified or updates involved, including code exchange, then, Analytics code updation could become a tough process. In such a situation, you can use the Google Tag Manager for a transition to Analytics.
The effort involved in implementing Google Tag Manager is almost similar to that involved in updating the Analytics code to your site each page. But, once you placed GTM code on your site then for all your future improvisations, the process will be simple and easy. You do not have to make the update for each page on your website, once applied to a page – it will apply to all other pages.
Do not confuse Google Tag Manager with Google Analytics as either of them is not the replacement for the other, but Google Tag Manager brings about modifications to how you implement Google Analytics on your site.
Speed for implementation
The Google Tag Manager is responsible for speeding up various processes. Without bringing about any change to the existing codes of your website, you can add changes and new tags with the help of Google Tag Manager. Marketers would really love the awesomeness of the tool as it helps in speeding up the set-up time, the testing and deployment of each edit is done automatically once the set up is ready. Once you have a better idea of Google Tag Manager, you can set up this all by yourself, without help from a developer.
Secure systems
Regardless of whatever problems or concerns effect a site, the security and site’s failure are the two factors that affect the most. But, with Google Tag Manager, this concern is solved as it takes care to prevent any kind of crashing of your website or vulnerabilities from cracking open for your site. For beginners, you can decide who will access your Google Tag Manager, Analytics accounts and annul who accesses the process at any given point of time. But, you are required to follow the standardized security practices as emphasized by Google Tag Manager as you would do with content management systems or web development tools – as needed. Utilize the standardized templates for common tagging scenarios, to reduce mistakes and scripting errors that might arise on your site.
Agility of Google Tag Manager
It provides you with an enormous amount of flexibility as you it requires a lesser amount of coding for any kind of complicated tags – while allowing you to utilize most out of your tags, without having to write a single line of code. This means you can get away with a little or no technical knowledge, but train yourself.
This tool is available FREE of cost and anyone can access and use it from anywhere at any time. you can signup to GTM from this link.
Debugging options
It is always an imperative part of your design process to ensure that all your tags are in functioning state before you get them published to the site and the site goes live. With the help of an in-built debug feature, Google Tag Manager provides you to manually test and debug the modifications made in your browser on your site before the site goes live. This would help you to reconsider what you publish preventing people from witnessing what you don’t want them to see. Chrome extensions, including Tag Manager Injector and Tag Assistant would help in making the debugging process much easier.

Version Control
It has become an impertinent part of every website, providing an in-built version control. Whenever you happen to modify a container, a new version would be created and archived. But, at a later point of time, if you want to retrieve the old version, you can do with ease. With this, you can troubleshoot any tagging issues and keep the tags organized as well.
Workspace and environment
If there are multiple people working on the same project, workspace and environment helps to divide spaces for creating tags. With this, you can organize your container and separate test tags that you do not wish to exhibit while your site goes live. This is specifically important when you want multiple teams to modify your website, along with stakeholders from outside the organization, who can modify and edit your site as well.
User access and permission
Google Tag Manager helps you to set up permissions and access rights for individual users. These permissions include edit, publish and view. Also, you can decide who has the ability to update the website internally and enable vendors to assist with tag and variable creation and trigger actions.
What more reasons do you need to use Google Tag Manager for your website? It will actually help in making the process easier and reduce the time and effort involved otherwise.
Aviv Digital is one of the leading digital marketing training institutes in Calicut, Kerala. We offer a wide variety of globally recognized certification programs that include SEO, SEM (PPC), SMM, Email Marketing and Inbound Marketing courses. For more details, Contact us at: +91 9037 489 577







